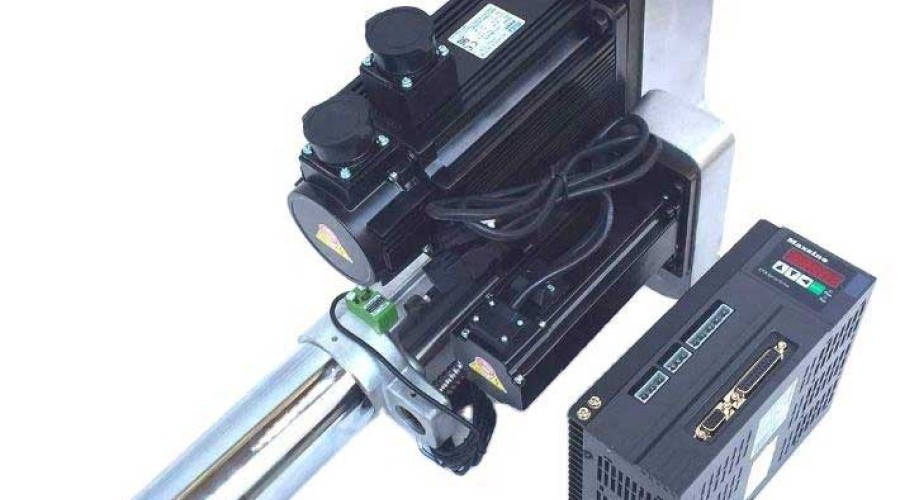

Servo motor
The word "servo" comes from the Greek word "slave". Servo in English is servo, which means that the system follows external instructions to perform the desired movement, achieving precise control of position, speed, acceleration and torque.
"Servo motor" can be understood as a motor that absolutely obeys the command of the control signal: before the control signal is sent, the rotor is stationary.
When the control signal is sent, the rotor rotates immediately and when the control signal disappears, the rotor can stop immediately.
Servo motors are the most widely used motors in the industrial automation industry.
The servo motor has the advantages of fast response, high precision, fast acceleration and deceleration, and the speed is not affected by the load.
It also has a wide speed range, good high-speed performance, stable low-speed operation, and has strong overload resistance and can withstand 3 times the rated torque.
Servo motor is a device that can convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
It can accurately control speed and position, and has the characteristics of fast response. It is usually used as an actuator in automatic control systems and is an important part of servo systems.
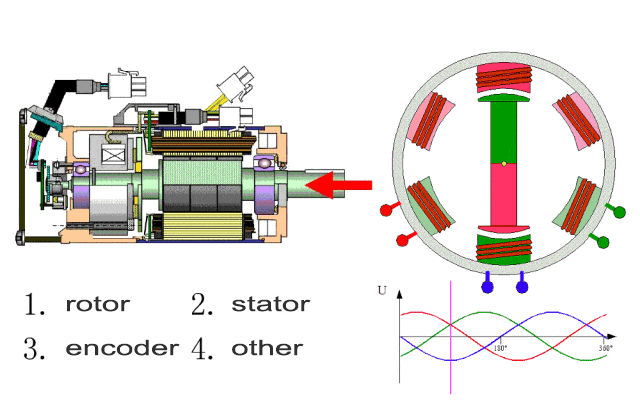
Internal structure
Internal structure of servo motor:
Servo motor is mainly composed of stator and rotor. There are two windings on the stator, the field winding and the control winding. The internal rotor is made of permanent magnets or induction coils, magnetically conductive materials, and the rotor rotates under the action of the rotating magnetic field generated by the excitation winding.
At the same time, the servo motor has its own encoder, and the driver receives the feedback signal from the encoder in real time.
Then adjusts the rotor rotation angle based on comparing the feedback value with the target value. It can be seen that the control accuracy of the servo motor is largely determined by the accuracy of the encoder.
Servo motors are mainly divided into two categories: DC servo motors and AC servo motors.
The two are different in structure and working principle, but they both have the characteristics that there is no rotation when the signal voltage is zero, and the rotation speed decreases at a constant speed as the torque increases.
Working principle
- The servo motor controls the magnetic field and current inside the motor by receiving the command signal from the controller, thereby generating torque to drive the motor to rotate.
- The rotor speed of the servo motor is controlled by the input signal. By changing parameters such as frequency, amplitude or phase of the input signal, precise control of the motor can be achieved.
- Servo motors have the advantages of fast response, high precision, and high stability, and are suitable for occasions that require precise control of position and speed.
Application
- Industrial robots:Servo motors are widely used in the field of industrial robots to realize robot joint motion, grabbing, transportation and other operations.
- CNC machine tools: Servo motors are important driving components of CNC machine tools and are used to control the movement of the machine tool spindle and feed axis.
- Automated production line: Servo motors are used to drive various conveyor belts, robotic arms, sorting devices, etc. in automated production lines.
- Aerospace: Servo motors are also used in the aerospace field, such as for controlling aircraft rudder surfaces, missile guidance systems.
Precision control strategy
Servo motor accuracy requirements: Servo motors require high-precision position and speed control to meet the needs of various industrial automation applications.
Analysis of influencing factors: The accuracy of servo motors is affected by many factors, including mechanical transmission errors, electrical control errors, environmental factors, etc.
- Mechanical transmission error: Due to factors such as manufacturing and assembly errors of mechanical transmission components, as well as wear and deformation during the transmission process, servo motor transmission errors will occur.
- Electrical control error: The accuracy and stability of the electrical control system have a great impact on the control accuracy of the servo motor. Factors such as current and voltage fluctuations may cause control errors.
- Environmental factors: Changes in ambient temperature, humidity, etc. may also affect the control accuracy of the servo motor.
- Optimize mechanical transmission design: By optimizing the design and manufacturing process of mechanical transmission components, reduce transmission errors and improve servo motor control accuracy.
- Improve electrical control accuracy: Use high-precision electrical control components and algorithms to improve the accuracy and stability of the electrical control system, thereby reducing control errors.
- Aiming at the impact of environmental factors on servo motor control accuracy, strengthen environmental adaptability design to improve the control accuracy of servo motors in various environments.










Leave a comment